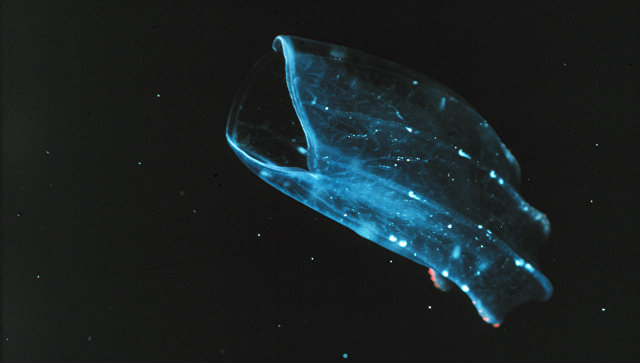
MOSCOW, April 10 - RIA Novosti . The first animals of the earth was not like sea sponges and hydras, today assumes the majority of scholars, and jellyfish and comb jellies, geneticists say in an article published in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
"Today, scientists collect large amounts of genetic information, analyze it, determine the relationship between its elements and then conclude that their findings are correct because of the improvements in the methods of analysis that are used. In 95% of cases it works, but in the remaining 5% the tree of evolution not going, "- says Antonis Rokas (Antonis Rokas) from Vanderbilt University in Nashville (USA).
Most modern groups and types of animals appeared about 540-520 million years ago, during the so-called "Cambrian explosion" - a sharp acceleration of evolution and increase the diversity of multicellular creatures. At this time it appeared the ancestors of worms, insects, fish and other vertebrates.
Traditionally, the first multicellular creatures on Earth were similar to modern hydraulic and sponges. They were arranged very primitive - they consist of only two layers and fed by passing through its water and filtering it from microbes, plankton and particles of organic materials.
Rokas and his colleagues say that such a statement was made on the basis of incomplete genetic data and incorrect analysis - in fact, the most ancient creatures on Earth are not the sponges and their relatives and ancestors of modern comb jellies and jellyfish. Similar statements have been made by geneticists in 2008, but then they are not taken seriously due to problems in the methodology of the study.
It tells Rokas, they came to this conclusion by using a completely different method of determining the shape of the "tree of evolution" that uses only common to all organisms, genes, rather than the entire set of them. In other words, the scientists took two potential candidates for the role of the ancestors of certain species, their shared genes were selected and determined how many similar regions of DNA have their potential offspring.
Such an approach, he says, allows you to avoid the appearance of false associations or disappearance of these relations, due to the sharp differences in the structure of a relatively unimportant genes. Taking one of two genes from analysis as Rokas notes, often leads to the fact that the relationship between the "questionable" organisms often reversed.
Following this idea, we analyzed the genetic kinship in 17 evolutionary tree of animals, fungi and plants, including the general evolution of the tree all multicellular beings.
As shown by this analysis, comb jelly and jellyfish, and not a sponge, are the ancestors of humans and other multicellular animals and turtles were relatives and birds, and crocodiles, and not only crocodiles, as previously thought, paleontologists.
Of course, the conclusions of Rokas and his colleagues are unlikely to convince all the supporters "gubochnoy" hypothesis, but researchers believe that their method of analysis is more accurate and less conflicting results than classical methods of phylogenetics.




No comments:
Post a Comment